Wibreathe: Estimating respiration rate using wireless signals in natural settings in the home
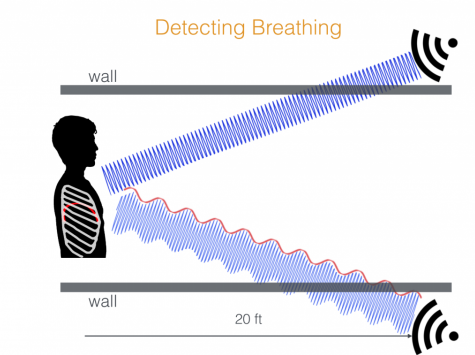
Sensing respiration rate has many applications in monitoring various health conditions, such as sleep apnea and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In this paper, we present WiBreathe, a wireless, high fidelity and non-invasive breathing monitor that leverages wireless signals at 2.4 GHz to estimate an individual’s respiration rate. Our work extends past approaches of using wireless signals for respiratory monitoring by using only a single transmitter-receiver pair at the same frequency range of commodity Wi-Fi signals to estimate the respiratory rate of an individual. This is done irrespective of whether they are in line of sight or not (e.g., through walls). Furthermore, we demonstrate the capability of WiBreathe in detecting multiple people and by extension, their respiration rates. We evaluate our approach in various natural environments and show that we can track breathing with the accuracy of 1.54 breaths per minute when compared to a clinical respiratory chest band.